CASI
By Boston Cell Standards | Funded by The National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health | Terms & Privacy
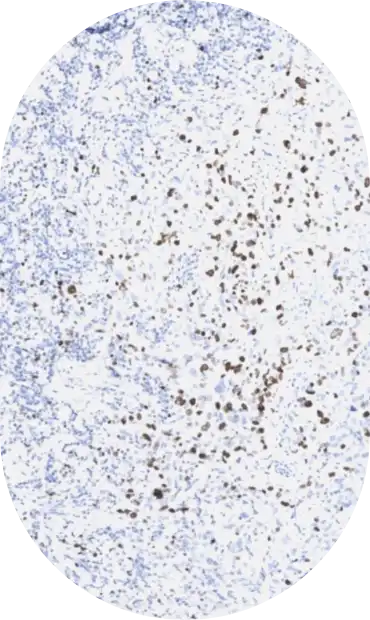
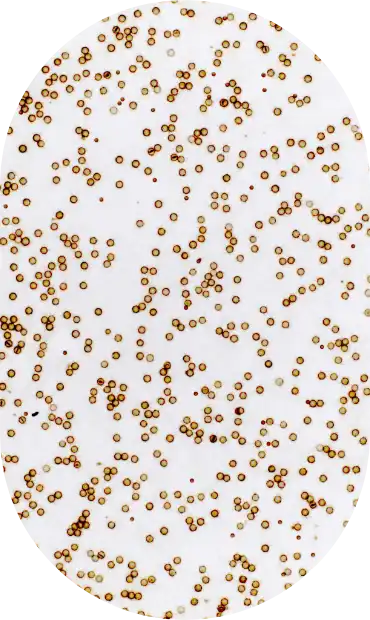
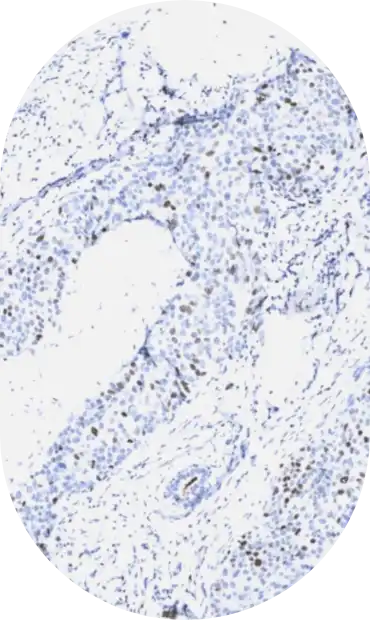
In the inaugural year, CASI will address analytic sensitivity thresholds for the following assays: HER2, PD-L1, p53, and BRAF.
The economic impact of inaccurate HER2 testing has been estimated to be in the billion-dollar range.1 The recent introduction of HER2-directed antibody conjugates, requiring even more accurate HER2 testing, further confounds this problem.2 The aim of this study is to identify the HER2 IHC assay analytic sensitivity that produces an optimal diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for responsiveness to HER2-directed cancer treatments.
Create a HER2 survey tool, a slide that bears both a HER2 tissue microarray (TMA) and HER2 calibrators expressing a range of HER2 concentrations.
Study Design. Test the survey tool under varying analytic sensitivities, at many IHC labs. Measure (a) diagnostic sensitivity/specificity from the TMA and (b) analytic sensitivity from the calibrators. Identify the analytic sensitivity range that yields the most accurate tissue test results.
IHC Gold standards. The determination of correct HER2 staining of the TMA cores will be based on (a) HER2 gene amplification, by ISH, and (b) use of multiple different lots of the same type of assay as used in the DESTINY-Breast04 clinical study.
Standardize the analytic sensitivity thresholds for accurately distinguishing:
More accurate HER2 test results will lead to better cancer patient care.
Create a PD-L1 survey tool, a slide that bears both a PD-L1 tissue microarray (TMA) and PD-L1 calibrators expressing a range of PD-L1 concentrations.
Study Design. Test the survey tool under varying analytic sensitivities, at many IHC labs. Measure (a) diagnostic sensitivity/specificity from the TMA and (b) analytic sensitivity from the calibrators. Identify the analytic sensitivity range that yields the most accurate tissue test results.
IHC Gold standard. The determination of correct PD-L1 staining of the TMA cores will be based on staining with 3 independent lots of the FDA-cleared PD-L1 PharmDx 22C3 FDA-cleared kit.
Higher lab-to-lab reproducibility by identifying objective assay analytic parameters for the PD-L1 PharmDx 22C3 assay that are associated with an accurate test result. Increased test accuracy and reproducibility leads to better decisions about treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
TP53 mutations identify a group of cancer patients that are likely to have a different clinical course and require different management. Variability in p53 IHC testing has complicated accurate patient testing for the mutation. This study aims to identify the p53 IHC assay analytic sensitivity that produces an optimal diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for predicting TP53 mutational status.
Create a p53 survey tool, a slide that bears both a p53 tissue microarray (TMA) and p53 calibrators expressing a range of p53 concentrations.
Study Design. Test the survey tool under varying analytic sensitivities, at many IHC labs. Measure (a) diagnostic sensitivity/specificity from the TMA and (b) analytic sensitivity from the calibrators. Identify the analytic sensitivity range that yields the most accurate tissue test results.
IHC Gold standard. The determination of TP53 gene mutational status is by DNA sequencing.
Higher lab-to-lab reproducibility by identifying objective assay analytic parameters associated with an accurate test result. Accuracy and reproducibility in p53 testing results in better cancer patient care, more accurately tailored to the genetics of their tumor.
Tumors containing a mutation in the BRAF gene often require treatment with BRAF inhibitors. Testing for the mutation by IHC is complicated by the lack of a standardized assay. The aim of this study is to identify the BRAF IHC assay analytic sensitivity that produces an optimal diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for predicting BRAF mutational status.
Create a BRAF survey tool, a slide that bears both a BRAF tissue micro-array (TMA) and BRAF calibrators expressing a range of BRAF concentrations.
Study Design. Test the survey tool under varying analytic sensitivities, at many IHC labs. Measure (a) diagnostic sensitivity/specificity from the TMA and (b) analytic sensitivity from the calibrators. Identify the analytic sensitivity range that yields the most accurate tissue test results.
IHC Gold standard. The determination of BRAF gene mutational status in the TMA is by DNA sequencing.
Higher lab-to-lab reproducibility by identifying objective assay analytic parameters associated with an accurate test result. Accuracy and reproducibility in BRAF testing helps oncologists more consistently prescribe BRAF inhibitors to the patient who need it.
Reference
By Boston Cell Standards | Funded by The National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health | Terms & Privacy